코딩하다 심심할때마다 맥북 하드웨어인포 가져오는 프로그램 코딩해볼까? 해서 시작했는데
처음에는 단순히 터미널에 sudo powermetrics --samplers smc -i1 -n1 같은 터미널 명령어들로 각 하드웨어 인포를
가져와서 출력문 스트링 파싱시켜 파이썬으로 간단히 처리해주고 나중에(귀찮아서절대안할듯) 쿼티로 ui 간단히 만들어서
연결하면 되겠지 싶어 시작한 개인 프로젝트 였습니다.
실제로 하드웨어인포 가져오는 mactemp 같은 라이브러리도 뜯어보면(필자는 macos 개발환경)
def CPU_Temp():
cpu_temp = [each.strip() for each in (os.popen('sudo powermetrics --samplers smc -i1 -n1')).read().split('\n') if each != '']
for line in cpu_temp:
if 'CPU die temperature' in line:
return line.strip('CPU die temperature: ').rstrip(' C')
return 'CPU Temperature not found'
위와 같이 간단히 import os 하고 popen으로 명령어로 받아서 긁어오는 구조로 생각보다 간단한(?) 아이디어입니다.
사실 코딩은 간단한 방식이 최고지만.. 뭔가 프로그래머의 로망은 좀더 딥하고 하드웨어단에서 놀고 싶단 말이죠..
그렇다고 일을 벌려서 pid 단위부터 처리하기는 귀찮고.. 그렇다고 간단하게 터미널에서 긁어오는건 수법(?) 같아서 싫다면
psutil을 이용하면 보기 좋게 간단하게 처리 할 수 있습니다,,
psutil (python system and process utilities)
실행중인 프로세서부터 CPU, 메모리, 네트워크, 디스크, 센서 등에서 뿌리는 정보를 가져다 쓸 수 있는
파이썬 라이브러리 중에 하나입니다.
주로 시스템 모니터링에 필요한 정보를 파싱해서 가져다 쓸 때 사용했습니다.
무엇보다 현재는 크로스플랫폼 라이브러리로 다음 OS 상에서 활용이 가능하도록 업데이트 되었습니다.
리눅스
윈도우
맥 OS
FreeBSD, OpenBSD , NetBSD
썬 솔라리스
AIX
간단히 사용법만 예시로 살펴보자면..
CPU
# CPU Info 예시
print("="*40, "CPU Info", "="*40)
# number of cores
print("Physical cores:", psutil.cpu_count(logical=False))
print("Total cores:", psutil.cpu_count(logical=True))
# CPU frequencies
cpufreq = psutil.cpu_freq()
print(f"Max Frequency: {cpufreq.max:.2f}Mhz")
print(f"Min Frequency: {cpufreq.min:.2f}Mhz")
print(f"Current Frequency: {cpufreq.current:.2f}Mhz")
# CPU usage
print("CPU Usage Per Core:")
for i, percentage in enumerate(psutil.cpu_percent(percpu=True, interval=1)):
print(f"Core {i}: {percentage}%")
print(f"Total CPU Usage: {psutil.cpu_percent()}%")메모리
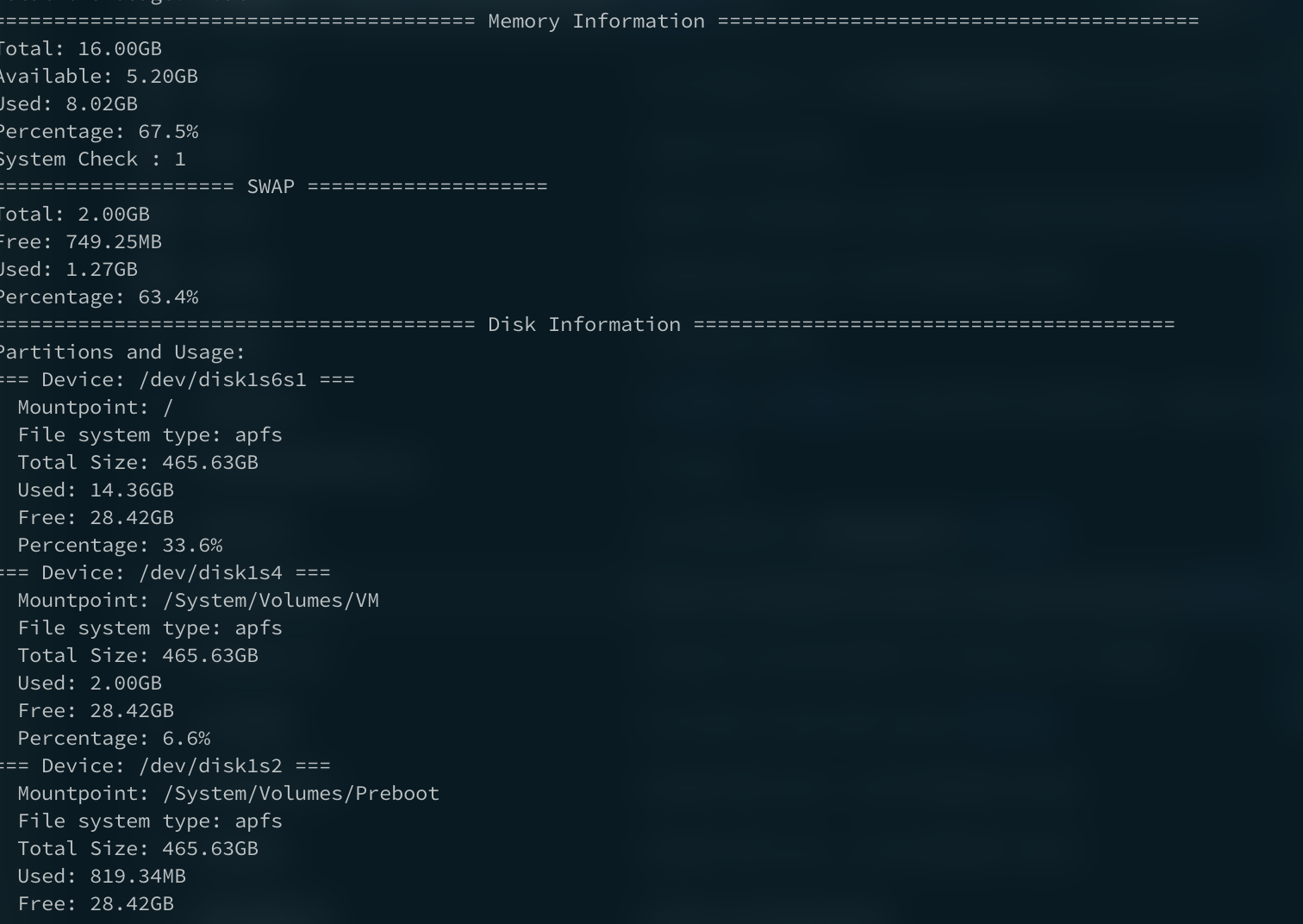
# Memory info 보기
print("="*40, "Memory Information", "="*40)
# get the memory details
svmem = psutil.virtual_memory()
print(f"Total: {get_size(svmem.total)}")
print(f"Available: {get_size(svmem.available)}")
print(f"Used: {get_size(svmem.used)}")
print(f"Percentage: {svmem.percent}%")
print("System Check : 1")
#스왑된 메모리도 가능!
swap = psutil.swap_memory()
print(f"Total: {get_size(swap.total)}")
print(f"Free: {get_size(swap.free)}")
print(f"Used: {get_size(swap.used)}")
print(f"Percentage: {swap.percent}%")네트워크
## Network info 가져오기
print("="*40, "Network Information", "="*40)
## get all network interfaces (virtual and physical)
if_addrs = psutil.net_if_addrs()
for interface_name, interface_addresses in if_addrs.items():
for address in interface_addresses:
print(f"=== Interface: {interface_name} ===")
if str(address.family) == 'AddressFamily.AF_INET':
print(f" IP Address: {address.address}")
print(f" Netmask: {address.netmask}")
print(f" Broadcast IP: {address.broadcast}")
elif str(address.family) == 'AddressFamily.AF_PACKET':
print(f" MAC Address: {address.address}")
print(f" Netmask: {address.netmask}")
print(f" Broadcast MAC: {address.broadcast}")
##get IO statistics since boot
net_io = psutil.net_io_counters()
print(f"Total Bytes Sent: {get_size(net_io.bytes_sent)}")
print(f"Total Bytes Received: {get_size(net_io.bytes_recv)}")위와 같은 느낌..
훨씬더 깔끔한 코딩과 쉬운 하드웨어인포값 사용이 가능합니다..
psutil라이브러리를 뜯어보면 직접 만드는것보다 라이브러리쓰는게 확연히 눈에 띄는 간편함..
더 많은 정보는 아래 공식 도큐에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
https://github.com/giampaolo/psutil
GitHub - giampaolo/psutil: Cross-platform lib for process and system monitoring in Python
Cross-platform lib for process and system monitoring in Python - GitHub - giampaolo/psutil: Cross-platform lib for process and system monitoring in Python
github.com
https://psutil.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
psutil documentation — psutil 5.9.5 documentation
Utility method retrieving multiple process information as a dictionary. If attrs is specified it must be a list of strings reflecting available Process class’s attribute names. Here’s a list of possible string values: 'cmdline', 'connections', 'cpu_aff
psutil.readthedocs.io
나중에 ui 단 까지 구현하면 한번 배포해볼까(?)..
그냥 귀여운 RunCat 애용합시다 :)

그냥 누가 만들어준거 쓰는게 세상에서 가장 편해..